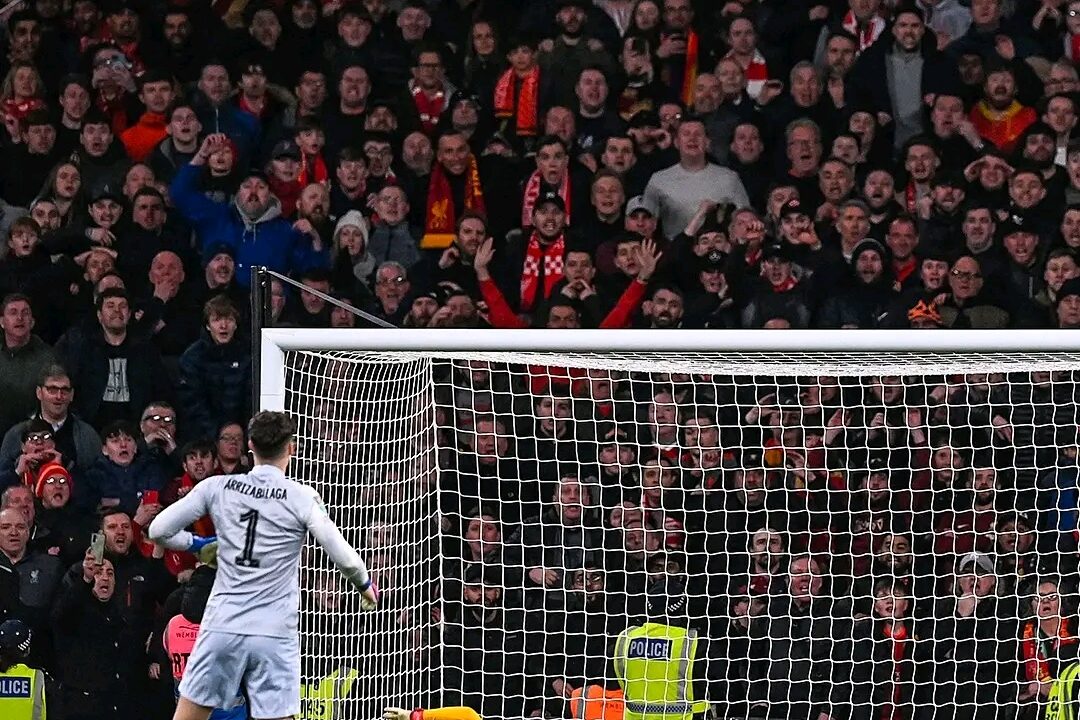
Penalty kicks in soccer, undoubtedly, are the most high-pressure moments in the game, often deciding the fate of an entire game, tournament, or even a World Cup. Yet, even the most formidable strikers succumb to this pressure and falter at times. Why does this happen? The answer isn’t just about technique. It’s about psychology, pressure and the mind games that play out in those painful seconds leading up to the kick.
From the moment the referee awards the penalty, a mental marathon begins for the taker. The walk from the halfway line is an eternity, every step echoing in the stadium. Self-doubt creeps in, fueled by the boos and cheers, the taunts of opponents, and the gaze of teammates waiting expectantly. Memories of past miss(es) flash across the mind, each one a potential sign of failure.
Research has shown that the more options a penalty taker has, the more difficult it can be to decide where to place the ball. From left to right, high to low, the more options there are, the more “analysis paralysis” the penalty taker faces, leading to a failure to execute. On the other hand, a well-thought-out strategy, while it may appear to reduce pressure, can become rigid if the goalkeeper sees the shot coming.
- The Pressure of Expectations
For strikers who live and breathe scoring goals, a missed penalty can feel like a personal betrayal, a public failure that weighs heavily on their shoulders. The pressure to succeed, amplified by the media, fans, and teammates, can become an unbearable burden, leading to a self-fulfilling prophecy of error. Learning to manage these expectations, developing a resilient mindset, and accepting that even the best miss sometimes are crucial aspects of a penalty taker’s mental arsenal.
- Anxiety
Anxiety is a common emotion that penalty takers and goalkeepers may experience during a penalty shoot-out. Anxiety is a state of nervousness, worry, or fear that can impair one’s cognitive and motor functions. Penalty takers may feel anxious because they have a lot of responsibility and pressure to score, and they may fear the consequences of missing the shot, such as disappointing their teammates, fans, or country. Goalkeepers may also feel anxious, but they have less to lose and more to gain, as they are not expected to save every penalty. Anxiety can affect penalty kicks in several ways, such as reducing accuracy, speed, and coordination, increasing muscle tension, and impairing concentration and decision making. Therefore, penalty takers and goalkeepers need to find ways to cope with anxiety, such as breathing exercises, relaxation techniques, positive self-talk, and visualization.
According to a study by Jordet et al. (2009), anxiety can have a negative impact on penalty performance, especially in high-pressure situations. The study analyzed 409 penalty kicks from 37 shoot-outs in World Cup and European Championship tournaments from 1976 to 2008. The results showed that the success rate of penalty kicks decreased from 92% in the first round to 80% in the fifth round, indicating that anxiety increased as the shoot-out progressed. The study also found that players who expressed more anxiety before taking the kick, such as looking down or away from the goal, had a lower success rate than those who expressed more confidence, such as looking at the goal or the goalkeeper.
- Confidence
Confidence is another important factor that can influence penalty kicks. Penalty takers and goalkeepers need to have a high level of confidence, as it can enhance their performance and reduce their anxiety. Confidence can be influenced by previous experiences, feedback, preparation, and self-talk. Penalty takers and goalkeepers can boost their confidence by recalling their past successes, receiving encouragement from their coaches and teammates, practicing their skills, and using affirmations and motivational statements. Confidence can also affect the choice of the spot and the direction of the shot. Penalty takers should choose their preferred spot and stick to it, as changing their mind at the last moment can reduce their confidence and accuracy. Goalkeepers should use their confidence to anticipate the direction of the shot and react faster.

A study by Wood and Wilson (2010) examined the effects of confidence and self-efficacy on penalty performance. The study involved 20 experienced soccer players who took 10 penalty kicks each under two conditions: high confidence and low confidence. The high confidence condition involved positive feedback, imagery, and self-talk, while the low confidence condition involved negative feedback, distraction, and doubt. The results showed that the players scored significantly more goals in the high-confidence condition than in the low-confidence condition, and also reported higher levels of self-efficacy and enjoyment.
Read Also: Between the Number 10 and 8, Who Has a Bigger Role to Play?
- Motivation
Motivation is another factor that can affect penalty kicks. Penalty takers and goalkeepers need to have a strong motivation to succeed, as it can increase their effort, persistence, and concentration. Motivation can be intrinsic or extrinsic. Intrinsic motivation is based on personal interest and enjoyment, while extrinsic motivation is based on external rewards and pressures. Intrinsic motivation is usually more beneficial, as it can foster a positive attitude and a growth mindset. Penalty takers and goalkeepers can enhance their intrinsic motivation by focusing on the fun and challenge of the task, rather than on the outcome or the expectations of others.
An experiment investigated the relationship between motivation and penalty performance; and the study involved 40 male soccer players who took five penalty kicks each under two conditions: intrinsic motivation and extrinsic motivation. The intrinsic motivation condition involved playing for fun and personal satisfaction, while the extrinsic motivation condition involved playing for money and social recognition. The results showed that the players scored more goals and had more positive emotions in the intrinsic motivation condition than in the extrinsic motivation condition, and also had higher levels of self-determination and perceived competence.
- Attention
Attention is another factor that can influence penalty kicks. Penalty takers and goalkeepers need to have a good attentional control, as they have only a few seconds to act. Attention can be internal or external. Internal attention is focused on one’s own thoughts and feelings, while external attention is focused on the environment and the task. External attention is usually more effective, as it can prevent overthinking and choking. Penalty takers should focus on the target and the ball, while goalkeepers should focus on the ball and the taker’s body language. Penalty takers and goalkeepers should also avoid distractions, such as the crowd, the opponents, or the stakes of the game.
A study involving 24 soccer players who took 10 penalty kicks each under three conditions: internal focus, external focus, and control are as follows. The internal focus condition involved focusing on the movement of the kicking leg, the external focus condition involved focusing on the movement of the ball, and the control condition involved no specific instructions. The results showed that the players scored more goals and had higher kick velocities in the external focus condition than in the internal focus condition, and also had lower levels of anxiety and perceived exertion.
Paradoxically, over-thinking can also be a culprit. A well-trained player has taken thousands of penalties in practice, and they usually perform better when they allow these practiced routines to take over – a phenomenon known as muscle memory. But in a high-pressure game, players often over-analyze the situation, disrupting their instinctive response and thereby their accuracy.. Decision making can be influenced by several factors, such as information, intuition, strategy, and pressure. Penalty takers should decide their preferred spot and stick to it, as changing their mind at the last moment can reduce their confidence and accuracy. Goalkeepers should use their intuition and experience to guess the direction of the shot, as they have little time to process the information. Penalty takers and goalkeepers should also have a strategy, such as varying their shots or dives, to increase their unpredictability and chances of success.
An analysis conducted in 2017 showed the decision-making of penalty takers and goalkeepers in the 2014 World Cup. The study used a game-theoretic model to examine the optimal strategies for both players, based on the probability of scoring and saving in each zone of the goal. The study found that the optimal strategy for penalty takers was to aim for the top corners of the goal, as they had the highest scoring probability and the lowest saving probability. The optimal strategy for goalkeepers was to dive to the left or right side of the goal, as they had the highest saving probability and the lowest scoring probability. The study also found that both players deviated from their optimal strategies in some cases, due to factors such as pressure, fatigue, or emotions.
In the end, penalty kicks are not only a test of physical ability, but also a test of mental strength. Many psychological factors can influence the performance of penalty takers and goalkeepers, such as anxiety, confidence, motivation, attention, and decision-making. These factors can explain why some great strikers may miss penalty kicks, and why some goalkeepers may save them. Penalty takers and goalkeepers need to master these psychological factors, as well as their physical skills, to perform well under pressure and achieve their goals.